How to Use the Aging of Accounts Receivable Method for Bad Debts
How to Use the Aging of Accounts Receivable Method for Bad Debts

These guidelines help ensure that the financial statements present a realistic and fair view of the company’s financial health. That means you wouldn’t record an unpaid debt as income on financial statements, so you wouldn’t need to cancel out unpaid receivables by listing bad debt expenses. You’ll calculate your bad debt allowance for each aging bucket then add these totals all together to find your ending balance. Here’s an example of an accounts receivable aging report with collection probabilities that add up to a total bad debt reserve. You’re only required to record bad debt expenses if you use the accrual accounting method since this method recognizes credit sales as income when earned.
How to Calculate Bad Debt Expense
- To protect your business against bad debt, you could consider Trade Credit Insurance (TCI).
- All that you need to know is the amount of the invoice that you are writing off.
- While bad debt expense prepares a business for potential losses, actual bad debt occurs when invoices remain unpaid.
- Vivek Shankar specializes in content for fintech and financial services companies.
- By using a specific formula and studying your accounts receivable aging report, you protect your company’s income.
- By summing up these amounts, you can ascertain the overall total of anticipated bad debts, which can then be allocated to the allowance account.
- The accounting treatment ensures that a company’s financial position and performance are accurately reflected.
This entry increases the bad debt expense on the income statement and establishes or adjusts the allowance for doubtful accounts on the balance sheet. Overall, following GAAP requirements for bad debt expense is essential for maintaining the credibility, transparency, and reliability of a company’s financial reporting. Understanding your bad debt expenses allows https://paulkiruiphotography.pa-desk.com/gross-profit-what-it-is-and-how-to-calculate-it/ your business to plan ahead, determine lost income, and help prevent cash flow issues. If you have several, you run the risk of misstating your net income every time the bad debt entry happens in a different period than the sales entry.
Invoice
The bad debt expense reverses recorded revenue entries in subsequent accounting periods when receivables become uncollectible. For example, for an accounting period, a business reported net credit sales of $50,000. Using the percentage of sales method, they estimated that 5% of their credit sales would be uncollectible. Under this approach, businesses find the estimated value of bad debts by calculating bad debts as a percentage of the accounts receivable ending balance. The allowance method helps businesses estimate how much of their accounts receivable may eventually become uncollectible. Unlike the direct write-off method, this approach anticipates losses before they occur, using historical data or customer trends to make bad debt expense calculator an informed guess.
Try Our Free Accounts Receivable Calculators
- GAAP encompasses various principles, assumptions, and guidelines that govern how financial transactions and events are recorded and reported.
- On the income statement, bad debt expense is reported as an operating expense, reducing the company’s net income.
- In general, the longer a customer prolongs their payment, the more likely they are to become a doubtful account.
- CEI directly impacts cash flow, financial stability, and receivables management.
- But you need to know how to calculate the bad debt expense percentage to estimate what your allowance should be.
Payment arrangements can help remove bad debt from the expense column on your ledger. When someone struggles to make payments, granting a reduction in the interest or offering extra time may be all they need to catch up. But you still have to acknowledge that it happens—even if it doesn’t happen often.

So if your bad debt rate was 2%, you can move 2% of your current credit sales into your bad debt allowance. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are a set of accounting standards and guidelines that companies in the United States must follow when preparing their financial statements. It’s almost the same formula as above, but the unknown variable has changed, and you’re calculating for the current period instead of looking at your historical averages. Now, you can use this percentage to estimate bad debt for your current period and determine your bad debt reserve. The idea of using the allowance method is to understand how much bad debt your business is likely to incur so you can plan ahead.
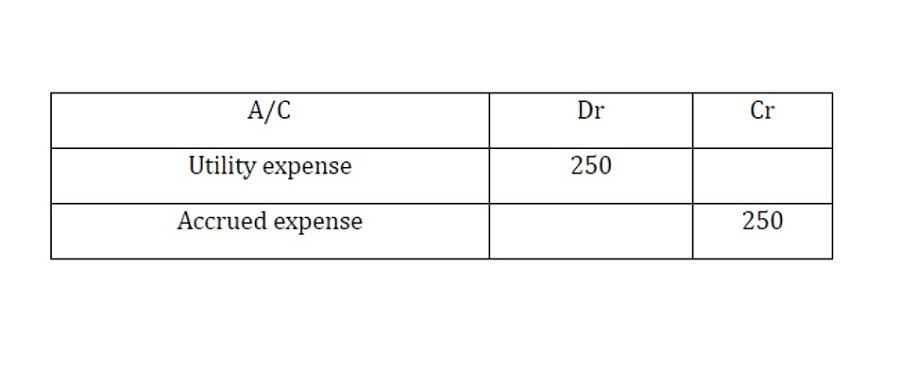
- You would record bad debt expenses in a bad debt expense account as soon as you realize a debt is uncollectible.
- The allowance method is the preferred accounting approach under GAAP for recognizing bad debt expense.
- A collaborative AR tool like Versapay combines cloud-based collaboration features with what you’d expect from a first-rate accounts receivable automation solution.
- Usually, the longer a receivable is past due, the more likely that it will be uncollectible.
- The risk classification becomes more accurate based on the customer’s payment history.
- The term bad debt refers to these outstanding bills that the business considers to be non-collectible after making multiple attempts at collection.
- The calculator also assists in calculating metrics like net realizable value, analyzing the allowance for doubtful accounts, and preparing journal entries for bad debt expense or write-offs.
Now let’s imagine that sometime later, a client tells you they won’t be able to pay the $2,000 they owe you. It’s a great way to visualize where your accounts receivable are piling up. You can then attribute a percentage of bad debt to each petty cash of these categories. Use the calculator above to input different values and see the bad debt expense and total receivables change dynamically. The results will help you make informed decisions based on the data you have. By referring to these guidelines, sources, and further readings, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of how to calculate and manage bad debt expense under GAAP.
Pro Tips to Prevent Bad Debt Expenses
This method categorizes accounts receivable based on the length of time they have been outstanding and applies different percentages of uncollectibility to each category. Older receivables typically have a higher likelihood of becoming uncollectible, so higher percentages are applied to them. This method provides a more accurate estimate of bad debt expense by considering the aging structure of receivables. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) provide a comprehensive framework for financial accounting and reporting. These standards are designed to ensure consistency, transparency, and comparability in financial statements across different companies.
- This entry adjusts the allowance for doubtful accounts to the required level, ensuring that the financial statements accurately reflect the estimated uncollectible receivables.
- When using the allowance method, you’ll create a journal entry to recognize bad debt expense and adjust the allowance for doubtful accounts.
- Clear guidelines can help reduce confusion about when you expect payment and what penalties may apply when an invoice goes unpaid.
- This method is straightforward but might lead to confusing accounting entries.
- For pinpointing risky accounts, the specific identification method sums up the total of such accounts, offering a customized reserve.
- Companies retain the right to collect these receivables should conditions change.
How To Calculate Bad Debt Expenses: A Comprehensive Guide

These methods often use past data or reports on how old the receivables are. Looking at companies like Dell Inc., Apple Inc., and Cisco Systems shows the ups and downs of handling accounts receivable. The total allowance is calculated by summing up the uncollectible amounts across all aging categories. This method categorizes accounts receivable based on how long they have been outstanding and applies different percentages to each category.